Home>>News
Machineryshops.com
Flexible add-on for sinking aquafeed extrusion
Though extrusion is proven the most efficient way to produce high quality fish feed, it is important for the process technology to react quickly and flexibly to new directions, since different types of fish demand different types of feed.According to the feeding behaviors of different aquatic species, aquatic feeds fall into three categories: floating, sinking and slow sinking. Both floating and sinking feed can produce satisfactory growth, but some fish species prefer floating, others sinking. Shrimp, for example, will not accept a floating feed, but most fish species can be trained to accept a floating pellet. The floating/sinking characteristics are distinguished by the bulk density of feeds. Bulk density of feed pellets after passing through the die ranging from 320g/l to 400g/l is floating feed, while within 390-410 g/l is slow sinking feed and in the scope of 450-550g/l is sinking product.
Technologies to extrude sinking aquafeed
A principal advantage of using extrusion cooking to make aquatic feeds is that it permits sinking and floating diets to be produced on the same equipment. Levels of starch and fat in formula also make their contribution to the floatability of aquafeed, but the main factors that influence feed density are temperature and pressure in the extruder barrel, which in turn, affect the expansion ratio.
Since extrusion is a high temperature, high pressure process, it is easier for an extruder machine to produce the low bulk density and high expansion floating feed than the unexpanded, but fully cooked sinking feed. It is because all parameters, which have a positive influence on increased bulk density, have a negative influence on starch cook, as increasing the bulk density in aquafeed in principle is a matter of reducing SME (Specific Mechanical Energy) and thus the starch cook. In addition, the reduced SME would decrease the pressure in the extruder barrel, and production capacity would be decreased due to declined pressure that insufficiently to force feed mash to pass through die holes.
Several process tools and add-ons are developed to control the bulk density of extrusion aquafeed,e.g. by changing the level of fat in feed formula or in post application process, controlling specific mechanical and thermal energy inputs, adding a vented barrel prior to discharge, adjusting die restriction, etc.
FAMSUN Bulk Density Control System
FAMSUN brand SMTZ Bulk Density Control System is developed to reduce product temperature, moisture, and expansion after a significant cook has taken place, in order to make a sinking product. It not only adds flexibility to extrusion production, but also has been proven to be an effective tool in improving production capacity, saving energy input and well controlling emissions.
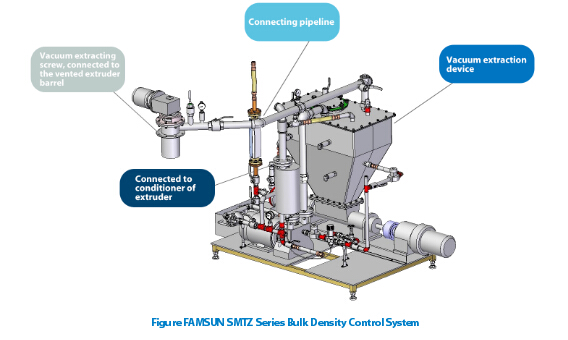
The system mainly consists of a vacuum extracting screw and a vacuum extraction device (see Figure). When it working, vacuum extracting screw connected to the vented barrel would take part of the steam away from the hot and wet feed mash after high-shear cooking. Steam took not only moisture but also energy with it, which helps to reduce product temperature, moisture, and pressure in reasonable range before discharging and thus the expansion ratio. On the other hand, the screw structure can prevent feed mash from flowing out of the vent under vacuum condition. Thanks to the bulk density control system, the extruding machine can not only produce sinking feed of high gelatinization level, but also increase extrusion capacity by 10-20%.
The steam took by extracting screw then is transported to the pressure tanks of vacuum extraction device. The vacuum extraction device not only serves the function of vacuum creation, but also for steam recycling. The steam took from extruder machinery barrel would be sent to the conditioner for conditioning production, which contributes to better conditioning quality and energy efficiency. Emissions such as fish meal odor or particles that liable to escape into the air when extruded out of die and vaporing together with steam now are well controlled. In the whole course, only recyclable water and little electrical energy inputs are required to sustain the system working at its best performance (see Table Energy inputs needed for density control).
The structure with two pressure tanks is a clever design. It allows for maintenance and cleaning can be carried out in one of the tanks with the other one keeping working at the same time. The liquid level alarming and adjusting switches in the tanks also guarantee that the system is of powerful vacuum creation ability all the time.
Reviews
Write a review
If you would like to write a review, please login first.